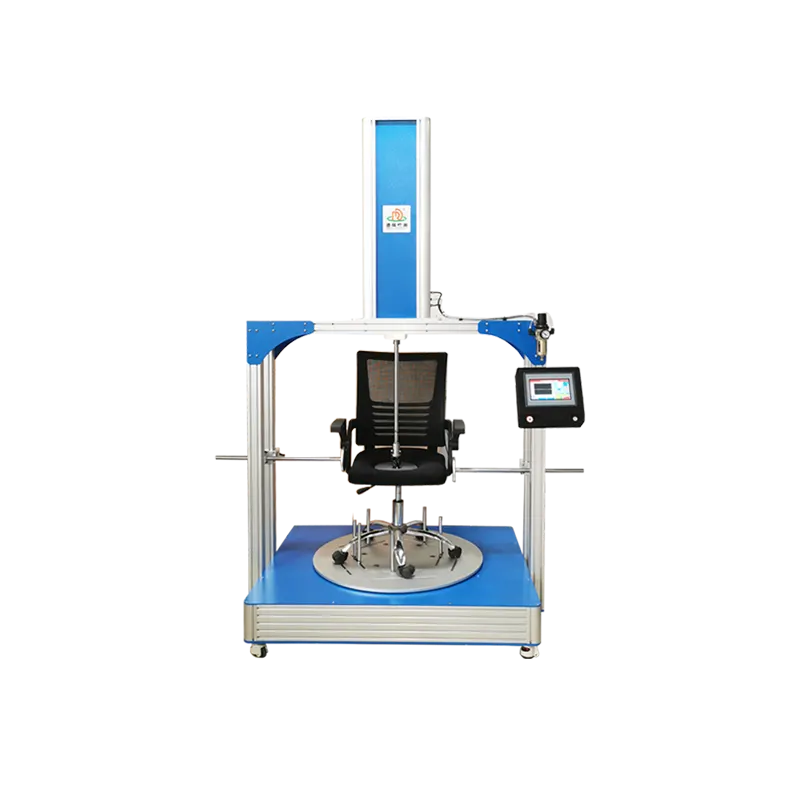
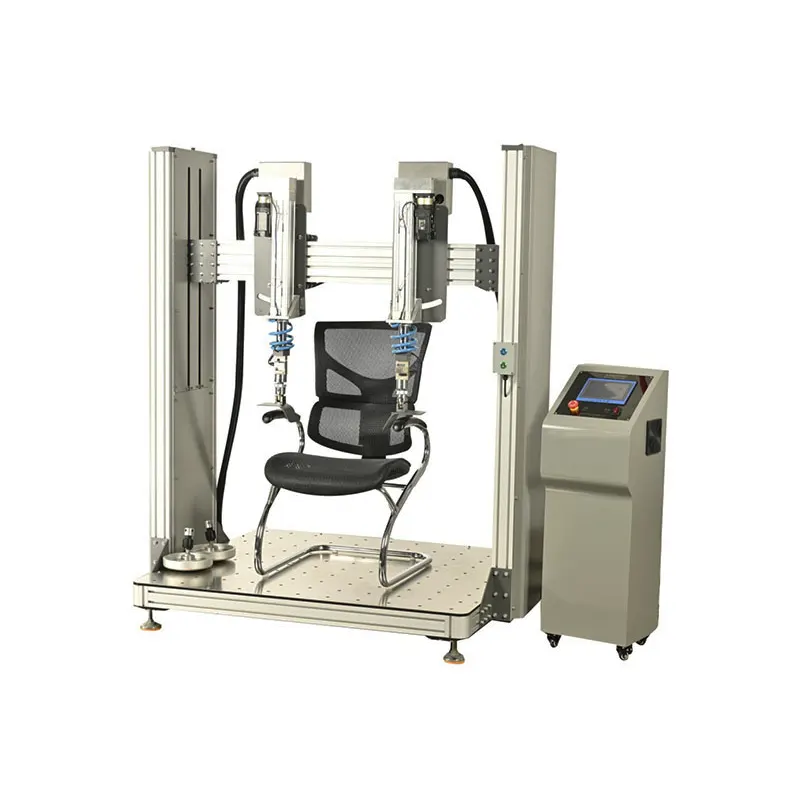
I. Product Overview
1.1 Definition and Applications
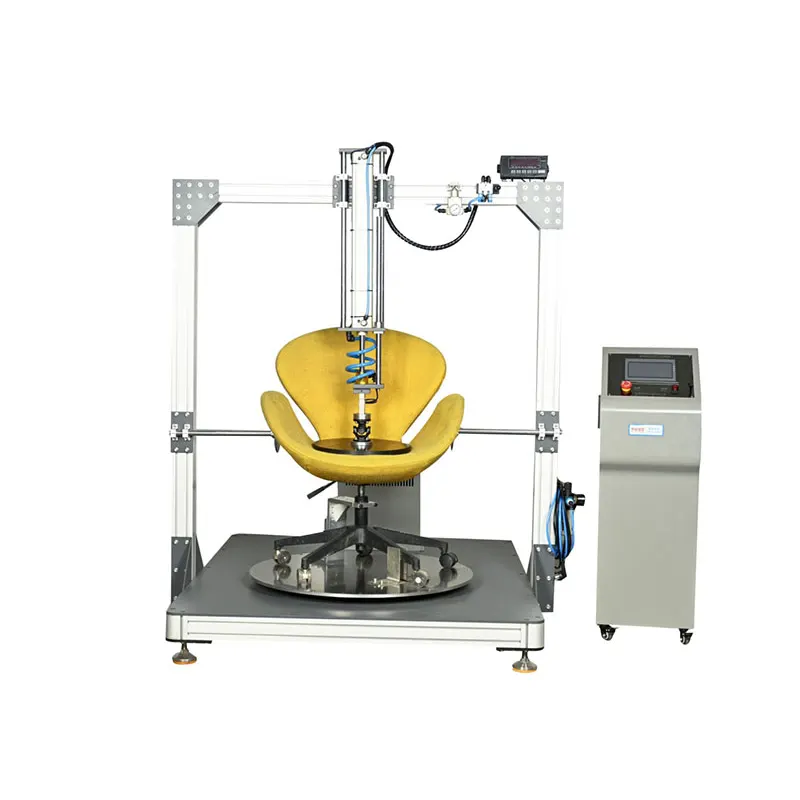
- •Core Definition: An automated testing device specifically designed to simulate the dynamic loads (e.g., human leaning, repeated pressing, tilt adjustment) that seat backs endure during long-term use, aimed at evaluating the structural strength, stability, and fatigue life of the backrest.
- •Target Scenarios: Suitable for backrest durability validation across various fields, including automotive seats (passenger cars/commercial vehicles), office chairs (ergonomic chairs/adjustable-height chairs), home furniture seats (sofas/massage chairs), and aviation/railway seats.
- •User Groups: Seat manufacturers (R&D/quality inspection departments), third-party testing institutions, material laboratories, and standard certification bodies (e.g., ISO/GB/SAE).
1.2 Development Background and Pain Points
- •Industry Demand: With the increasing complexity of seat functions (e.g., electric adjustment, multi-angle support, lightweight design), backrests must withstand more frequent dynamic loads. Consumers’ heightened requirements for safety and comfort further drive the need for enhanced durability testing.
- •Limitations of Traditional Testing: Manual simulation of loads is inefficient and inconsistent; general-purpose testing equipment cannot adapt to different seat structures (e.g., irregular backrests, special connection points); lack of data-driven analysis capabilities, making it difficult to provide design optimization insights.
Applicable Scope of Seat Back Durability Tester
The seat back durability tester is primarily used to evaluate the durability of seat backs under repeated use. Its applicable scope is broad, covering various types of seats and different application scenarios. The details are as follows:
Applicable Seat Types
- •Automotive Seats: Whether for passenger cars, commercial vehicles, or public transportation such as buses and subways, the seat backs require durability testing. In daily use, passengers frequently adjust the backrest angle or lean against it. The tester simulates these actions to assess the long-term reliability of the seat back, ensuring passenger safety and comfort.
- •Office Chairs: Office workers spend long hours seated, often adjusting the backrest to relieve fatigue. The tester evaluates the durability of office chair backrests under prolonged use, body pressure, and frequent adjustments, ensuring product longevity and quality.
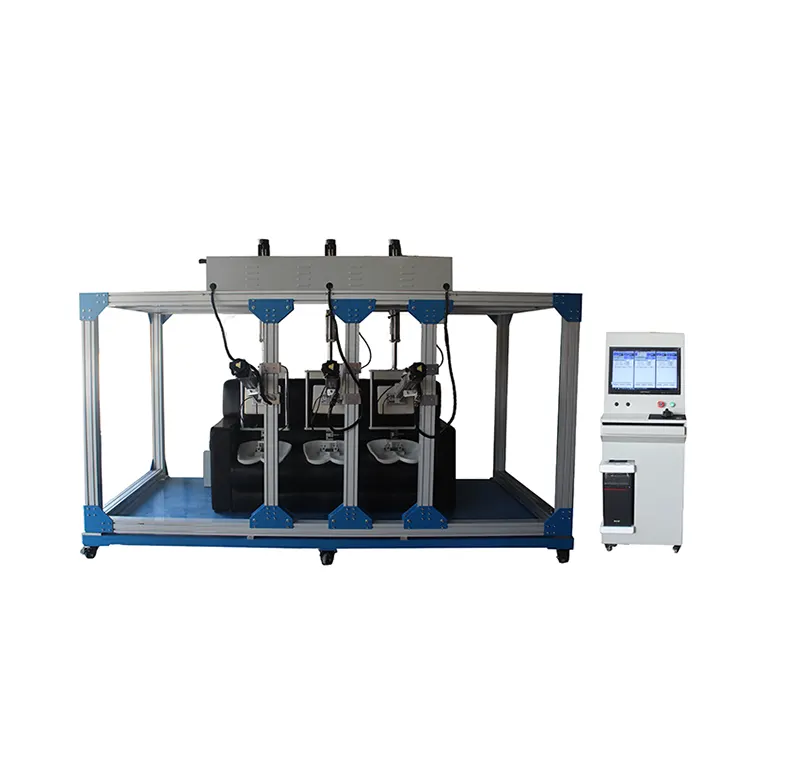
- •Home Furniture Seats: Includes sofas, lounge chairs, and other home seating. People frequently lean against these seats during rest or leisure, subjecting the backrests to varying degrees of pressure and friction. The tester simulates home-use conditions to assess the durability of home furniture seat backs, providing consumers with reliable products.
- •Aircraft Seats: During flights, passengers rely on seat backs for rest, and the seats must endure frequent takeoffs, landings, and turbulence. Testing the durability of aircraft seat backs ensures their safety and reliability under extreme conditions, safeguarding passenger comfort and security.
Core Components
- Power System
- Pneumatic Drive: The most common method. A stable air source is provided by an air compressor, and solenoid valves control the airflow direction and volume into the pneumatic cylinder, thereby driving the cylinder piston rod in a linear reciprocating motion. This method offers high force, relatively fast speed, and lower cost.
- Electric Drive: Uses a servo motor or stepper motor to drive an electric actuator (or ball screw) for precise linear motion. This allows for more precise control, programmable speed and position, and lower noise, but is typically more expensive.
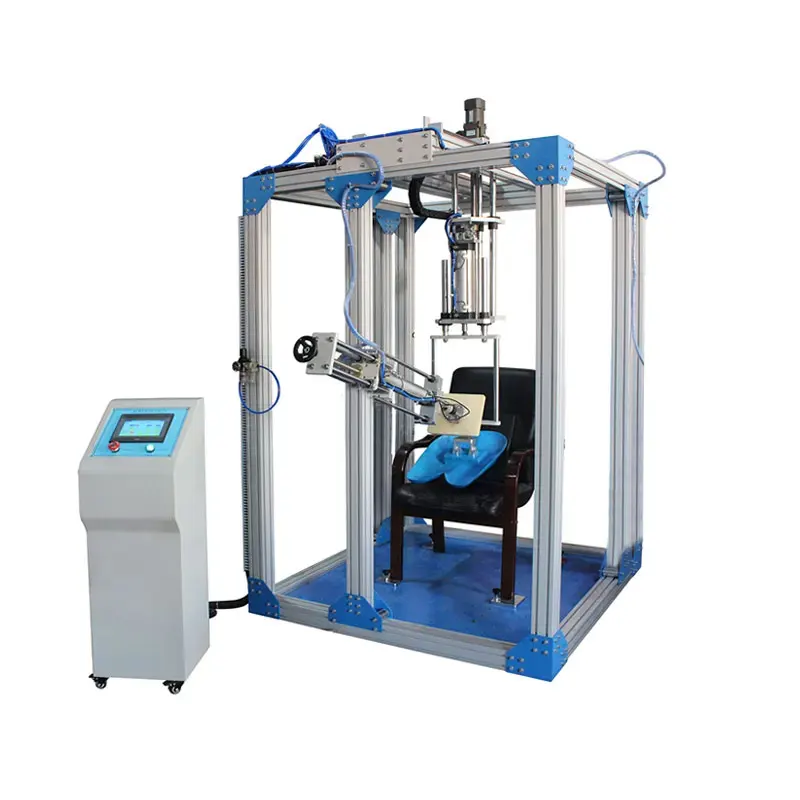
- Actuator
- Loading Module: Usually a contoured loading block or pad attached to the end of the cylinder/actuator piston rod. Its shape simulates the human back or lumbar region to apply force to a specific area of the seat back.
- Adjustment Mechanism: The equipment usually includes rails, sliding channels, and locking devices, allowing users to adjust the height, angle, and front-back position of the loading module flexibly according to the seat dimensions and test standard requirements, ensuring force is applied accurately to the correct location.
- Control System - The "Brain"
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): The core controller of the equipment. It receives commands from the operator (e.g., force value, cycle count, frequency) and precisely controls the solenoid valves or servo motors to direct the power system.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface) Touchscreen: The user interface. Operators set all test parameters here (e.g., test force, number of cycles, speed, dwell time) and monitor the test process in real-time (current cycle count, real-time force curve, equipment status).
- Sensing and Feedback System - The "Eyes and Nerves"
- Force Sensor: Usually installed between the cylinder piston rod and the loading module to monitor and feedback the actual force value applied to the backrest in real-time. The PLC compares this read value with the set target value and dynamically adjusts the air supply or current (for electric actuators) through a PID algorithm to ensure the applied force remains accurate and stable.
- Displacement Sensor/Encoder: Measures the stroke displacement of the cylinder piston rod, allowing precise control of the loading module's travel distance and position, preventing overtravel that could damage the sample or equipment.
- Limit Switches: Hardware safety devices that set the physical limits of motion to prevent accidental overtravel.
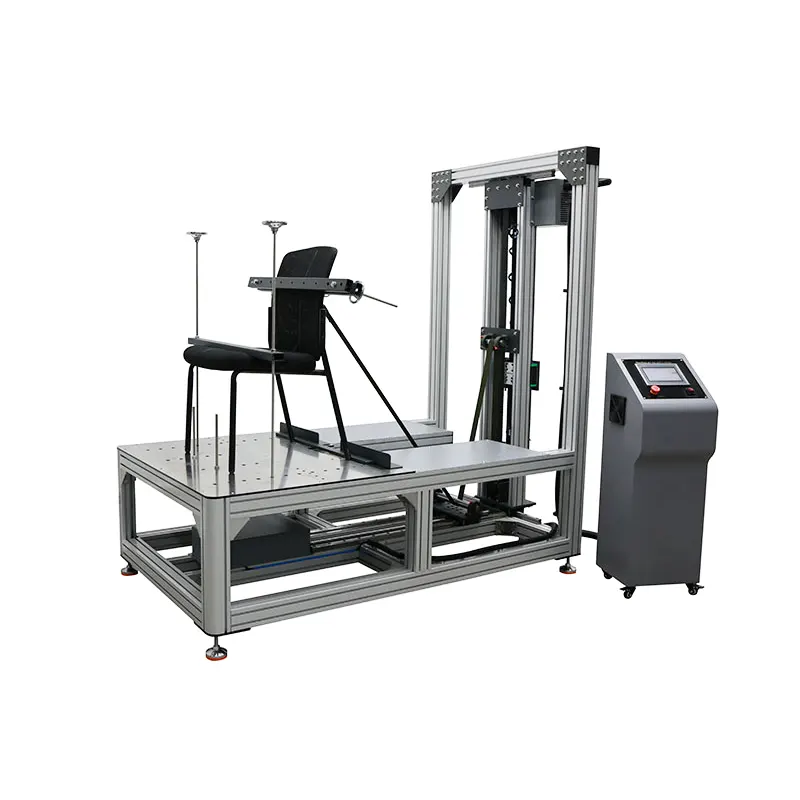
- Mechanical Frame and Fixtures
- A sturdy steel frame supports and fixes all components.
- Seat Fixtures: Used to securely clamp the test seat onto the platform, ensuring the seat does not move or tip over during testing, guaranteeing the repeatability and accuracy of the tests.
Features of the instrument
1. Adjustable Test Channels
The seat back fatigue tester features a manual lifting mechanism, allowing compatibility with chairs of various heights.
- •Minimum test height (seat compression): 550 mm
- •Maximum test height: 1300 mm
During assembly, our technicians will pre-adjust the optimal height based on your requirements. For manual height adjustment, simply use the lifting controller.
2. High-Quality Components
This machine is built with premium domestic and international parts, ensuring durability and precision:
- •Frame: APS high-strength aluminum alloy profile
- •Motor: Taiwan Bangshuo motor
- •Gearbox: Taiwan gear reducer
- •Cylinder: German FESTO pneumatic cylinder
- •Sensors, air hoses, solenoid valves, oil mist separators – all from renowned brands
3. Modular Design
The backrest loading force range is 0N–2000N.
To accommodate future market changes, updated standards, or non-standard testing requirements, the tester adopts a modular design.
- •If the current loading force capacity is insufficient, simply upgrade the cylinder module—no need for a full system replacement.
4. Power Failure Protection
Equipped with a power outage protection system, the tester:
- •Automatically saves current test data when power is lost.
- •Allows resumption of testing and viewing of previous data once power is restored.
5. Abnormal Condition Protection
The machine includes smart safety mechanisms:
- •Cylinder Stroke Limitation → Restricts the movement range of the backrest and seat testing cylinders.
- •Sensor Force Protection → Limits the maximum applied force. If the set force threshold is exceeded, the system automatically stops to prevent damage.
6. Stable Support & Easy Mobility
- •Firm & Flexible Base:
- •FUMA casters (industrial-grade wheels) for smooth movement, easy adjustment, and heavy-load capacity.
- •Integrated adjustable turntable provides:
- •Stable support
- •Leveling adjustment
- •Mobility
- •Shock absorption
- •Design: Ergonomic, sleek, and durable for long-term lab use.