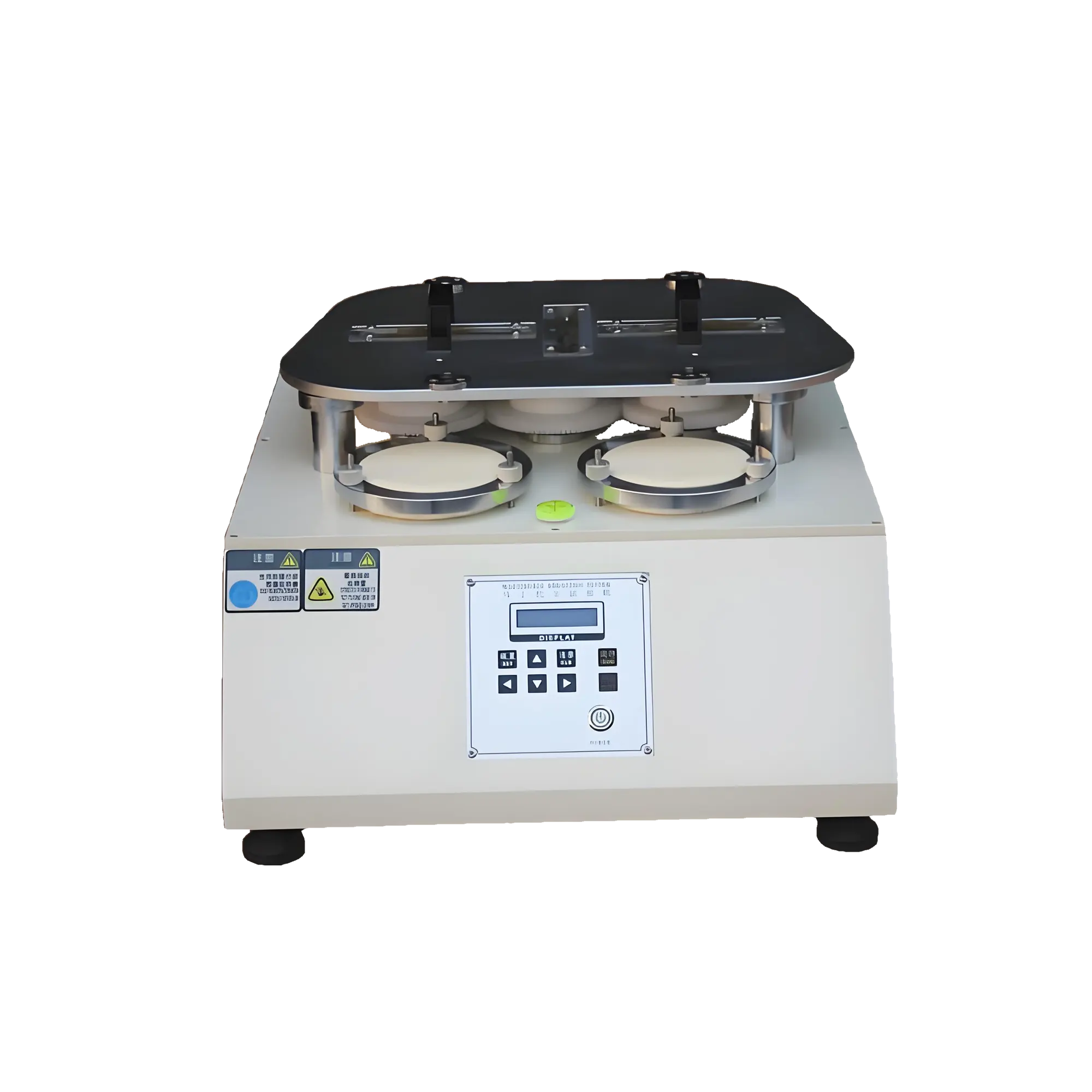
A DIN abrasion tester is a specialized instrument used to evaluate the wear resistance of materials, based on relevant German Industrial Standards (DIN). It simulates the friction that materials experience in real-world use to determine their resistance to abrasion. This testing is crucial for assessing the durability of materials such as leather, rubber, and plastics.
Working Principle
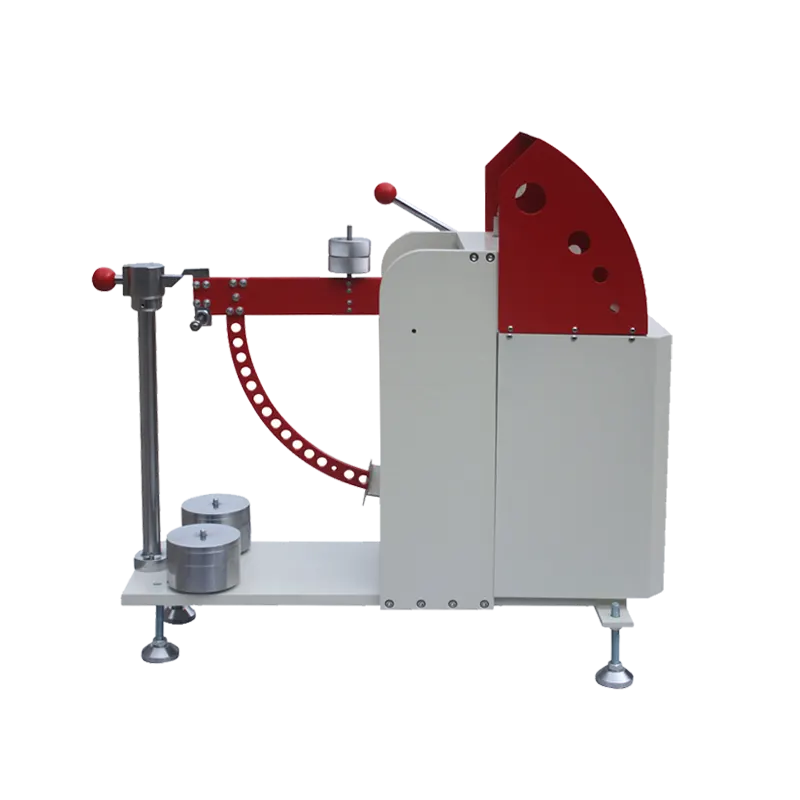
The tester typically uses a predefined abrasive (e.g., sandpaper) mounted on a grinding wheel. Under a constant load, the grinding wheel rotates and rubs against the test sample fixed on the testing platform. After a specified number of rotations or when a certain level of wear is reached, parameters such as mass loss, thickness change, or visual appearance of the sample are measured to evaluate its wear resistance.
Main Components
- •Grinding Wheel: The part that directly contacts and rubs against the sample. Its material, hardness, and surface shape are selected and designed according to different testing standards.
- •Loading Device: Applies a constant pressure on the grinding wheel to ensure stable friction force during testing. Loading methods may include weights, pneumatic, or hydraulic systems.
- •Sample Holder: Securely fixes the test sample to prevent movement or shifting during testing, ensuring accurate results.
- •Drive System: Rotates the grinding wheel at a specified speed, with stability being crucial for reliable testing.
- •Counter: Records the number of grinding wheel rotations or abrasion cycles to control the testing process accurately.
Applications
- •Leather Industry: Evaluates the wear resistance of leather products (e.g., shoes, bags, sofas) to ensure durability and resistance to scuffing or fading.
- •Rubber Industry: Tests the abrasion resistance of rubber tires, flooring, seals, and other products to ensure performance stability in various conditions.
- •Plastics Industry: Assesses the wear resistance of plastic sheets, pipes, films, and other materials for research and quality control.
- •Textile Industry: Though less common, some specialized fabrics (e.g., outdoor clothing, workwear) are also tested for abrasion resistance using this method.
Precautions
- •Sample Preparation: Sample size, shape, and preparation must strictly follow relevant standards to ensure representativeness and comparability.
- •Grinding Wheel Selection & Calibration: Choose the appropriate grinding wheel based on the test material and standard, and regularly calibrate or replace it to maintain proper abrasion characteristics.
- •Testing Environment: Factors like temperature and humidity may affect results, so testing should be conducted under controlled conditions.
- •Proper Operation: Operators should be familiar with the instrument’s usage and follow procedures carefully to avoid inaccurate results or equipment damage.
DIN 53516 Abrasion Standard
What is the wear standard of DIN 53516?
Both ASTM D5963 and DIN 53516 abrasion standards only require 10N of force to press the test specimen against the drum. However, the ISO 4649 abrasion standard allows for a reduced force of 5N or an increased force of 20N under special circumstances. The BS 903 abrasion standard is a British standard.
Is the DIN 53516 standard the same as ISO 4649?
The German DIN 53516 is an older standard that has been largely replaced by the ISO 4649 abrasion standard. However, DIN 53516 remains valuable and worth referencing, as some of its methods and specifications overlap with ISO 4649. Nevertheless, there are differences in testing requirements and applicable materials.
When does the DIN abrasion tester stop?
Any vibration may lead to inaccurate results. The machine stops after the test specimen has traveled a 40-meter abrasion distance, which corresponds to approximately 84 rotations of the rotating cylindrical drum. Operators conduct a series of tests using both the test rubber compound and a standard rubber reference.
How is abrasion resistance measured in the drum?
Abrasion Testing Method (ISO 4649 / DIN 53516)
The test is relatively simple. Abrasion resistance is measured by moving a test rubber sample against an abrasive sheet mounted on a rotating drum. The result is expressed as volume loss in cubic millimeters (mm³), such as 150 mm³.